Home |
News |
Research |
Publications |
People |
BoxLib |
Links |
Downloads |
December 2014 News
 |
Mueller, Day present at AGU 2014Juliane Mueller presented a poster at the 2014 AGU Fall Meeting on December 18 in San Francisco. Mueller's research primarily focuses on the development of surrogate model algorithms for computationally expensive optimization problems. Her poster, "Parameter Estimation in CLM4.5 Using Surrogate Model Based Global Optimization" showcased the application of her algorithms to calibrating a global climate model, in particular the CH4 module of the Community Land Model which is part of the Community Earth System Model. This research was done in collaboration with colleagues at Cornell University. |
|
 |
Marc Day co-authored a poster at the 2014 AGU Fall Meeting summarizing the status of the Amanzi project, the open-source multi-process "HPC Simulator" component of the DOE-sponsored ASCEM project. Amanzi target problems currently include multiphase subsurface flow and transport problems with complex geochemistry and geostatistical representations of natural and engineered waste containment systems. Amanzi is a unique application, in that it features the capability to select at runtime between structured-grid AMR (based on CCSE's BoxLib libraries), and unstructured mesh (based on the Trilinos framework). |
Emmett speaks at 2014 Bay Area Scientific Computing DayMatt Emmett gave a 20 minute talk at the 2014 Bay Area Scientific Computing Day, held on Saturday December 13 at Stanford University. His talk, "Accelerating Scientific Computing -- new approaches to numerical integration", introduced a novel hybridization of the multi-level Spectral Deferred Correction scheme and the Adaptive Mesh Refinement algorithm, and some recent results on a time-parallel integration scheme for molecular dynamics simulations. His work was done in collaboration with John Bell, Michael Minion, and Weiqun Zhang. |
 |
|
|
2015 ERCAP Awards - CCSE Researchers Awarded
|
Duarte Speaks at ESD Climate BrownBag SeminarMax Duarte gave the lunchtime "brown bag" seminar in the Earth Sciences Division on Monday, December 8. He spoke about his recent work with Ann Almgren and John Bell on low Mach number modeling of moist atmospheric flows. |

|
|
|
The BoxLib -- Clawpack ConnectionIn a recent blog about Clawpack turning 20, David Ketcheson notes that future plans for the Clawpack family of codes include work by Matt Emmett to enable massively parallel adaptive mesh refinement (AMR) in PyClaw by integrating BoxLib functionality. |
Combustion Simulations by Emmett, Zhang and Bell FeaturedRecent work by Matt Emmett, Weiqun Zhang, and John Bell is now featured at the LBNL Computational Research Department (CRD) website. The article describes results presented in a paper titled High-Order Algorithms for Compressible Reacting Flow with Complex Chemistry, that was featured on the cover of a recent issue of Combustion Theory and Modeling, a journal of the Combustion Institute. This paper describes a numerical algorithm for integrating the multicomponent, reacting, compressible Navier-Stokes equations, targeted for direct numerical simulation of combustion phenomena. See the article here. |
|
|
|
2015 INCITE Awards -- CCSE and Collaborators Awarded 50 Million HoursAnn Almgren, John Bell and a team of researchers have been awarded 50 million hours on the Titan Cray XK7 at Oak Ridge National Laboratory as one of the 56 2015 US DoE's INCITE awards. The two-year project, titled, Approaching Exascale Models of Astrophysical Explosions, is led by Professor Michael Zingale in the Department of Physics and Astronomy at Stony Brook University. The team, in addition to Zingale, Almgren and Bell, includes Alan Calder of Stony Brook University, Chris Malone of Los Alamos National Lab, Dan Kasen of LBNL and UC Berkeley, and Stan Woosley of UC Santa Cruz. The team is carrying out a comprehensive study of two classes of thermonuclear-powered stellar explosions involving compact objects, Type Ia supernovae (SNe Ia) and X-ray bursts (XRBs). Key to their analysis is the use of two multiphysics simulation codes developed in CCSE -- MAESTRO and CASTRO --- which are specifically designed for the efficient modeling of astrophysical explosions. "The team's primary goal of the project will be to explore a variety of initial configurations of stellar explosions in the densest stellar objects in the Universe," said Zingale. |
November 2014 News
Almgren Gives Invited Talk at APS-DFD Annual MeetingAnn Almgren presented an invited talk at the 67th Annual Meeting of the APS Division of Fluid Dynamics held in San Francisco. Almgren's talk was titled Low Mach Number Models for Stratified Flows, and described, in particular, work on low Mach number models for astrophysical flows, including results from simulations of convection and ignition in Type Ia supernovae using MAESTRO. |
|
 |
Bell Gives Invited Talk at the Codesign2014 Workshop in ChinaJohn Bell presented an invited talk at the fourth international workshop on "COllaborative DEvelopment of SIMulation software of next GeNeration (CoDesign 2014)" held at the National Supercomputing Center, Sun Yat-Sen University in Guangzhou, China. The meeting was part of HPC China. Bell, the Deputy Director of the ExaCT CoDesign Center, discussed his experience with codesign in a talk titled Combustion CoDesign Challenges at Extreme Scale. |
Chaudhri Gives Invited Talk at UC MercedAnuj Chaudhri recently presented a talk in the Department of Mechanical Engineering at UC Merced. The talk, titled Fluctuating Hydrodynamics of Multiphase Fluids, described work done with John Bell, Alejandro Garcia and Aleksandar Donev on developing numerical algorithms for the van der Waals fluctuating hydrodynamics equations and looking at problems in non-equilibrium such as spinodal decomposition and adiabatic cooling via the piston effect. |
|

|
Nonaka and Chaudhri Present at APS-DFD Annual MeetingAndy Nonaka and Anuj Chaudhri presented talks on their work at the 67th Annual Meeting of the APS Division of Fluid Dynamics held in San Francisco. Nonaka's talk was titled Efficient Modeling of Multicomponent Diffusive Mixing while Chaudhri's talk was on Modeling Multi-Phase Flow Using Fluctuating Hydrodynamics. |

|
Mueller Speaks at INFORMS Annual MeetingJuliane Mueller recently presented a talk on her research at the INFORMS Annual Meeting. The talk, titled MISO: Mixed-Integer Surrogate Optimization Framework, focused on her recently developed algorithm framework for global optimization problems that have computationally expensive black-box objective functions and whose variables are mixed-integer. This flexible framework allows the user to choose between different surrogate models that are used to approximate the computationally expensive objective function. Various sampling strategies are available within the framework and Mueller showed that a combination of stochastic sampling, a target value strategy, and local search yields high-accuracy solutions. Algorithms for mixed-integer computationally expensive black-box global optimization problems are very scarce and the MISO framework therefore extends this increasingly important research area. |

|

|
Emmett participates in (HPC)^3 workshop at KAUSTMatt Emmett recently participated in the 3rd (HPC)^3 workshop at KAUST, and gave a talk titled A novel Multilevel Spectral Deferred Correction (MLSDC) integration scheme for Adaptive Mesh Refinement (AMR) combustion codes. The talk described a novel hybridization of the multilevel structure of a block-structured Adaptive Mesh Refinement (AMR) algorithm with the multilevel structure of the Multilevel Spectral Deferred Correction algorithm (MLSDC). The resulting hybrid MLSDC+AMR scheme is high-order and less computationally expensive than a traditional sub-cycling method based on high-order SDC splitting. Emmett also participated in the AMR working group at the conference and was able to successfully wrap BoxLib's regridding routine with Python. This effort will eventually allow the PyClaw project to leverage BoxLib and incorporate AMR techniques into PyClaw. |
October 2014 News
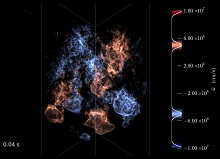
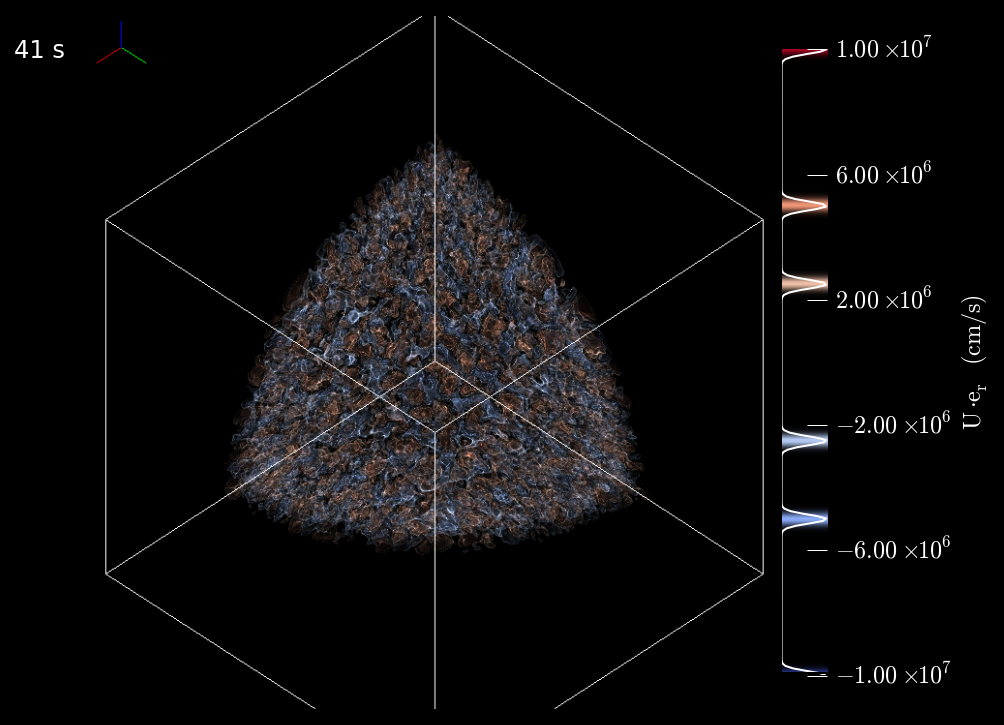
"Death Throes of a Star":CASTRO Simulation Featured as one of Nature's Images of the MonthA recent CASTRO simulation by UC Santa Cruz postdoctoral researcher Ken Chen has now been featured as one of Nature magazine's Images of the Month for October 2014. The caption reads: "The work suggests that a star about 55,000 more massive than the Sun would have blown itself apart, leaving no remnant behind, rather than collapsing into a black hole as astrophysicists have traditionally assumed." |
|
September 2014 News
|
CASTRO Simulations of Ancient Stars' Unusual Death FeaturedRecent CASTRO simulations by UC Santa Cruz postdoctoral researcher Ken Chen have been featured recently on the NERSC website, the US Department of Energy Office of Science website, and even the science section of the UK's Daily Mail. The simulations were run on machines at NERSC and the Minnesota Supercomputing Institute. See the full story here. The simulations were run on machines at NERSC and the Minnesota Supercomputing Institute. |
Chaudhri gives Invited Talk at SJSUAnuj Chaudhri presented a talk on Thursday, September 25 at the San Jose State University's Department of Physics & Astronomy seminar. The talk, titled Fluctuating Hydrodynamics of Multiphase Fluids, described work done with John Bell, Alejandro Garcia and Aleksandar Donev on developing numerical algorithms for the van der Waals fluctuating hydrodynamics equations and looking at problems in non-equilibrium such as spinodal decomposition and adiabatic cooling via the Piston effect. |
|
August 2014 News
|
|
Bell Named to National Academies' Board on Mathematical Sciences and Their Applications (BMSA)John Bell has just been named to a three-year term on the National Academies' Board on Mathematical Sciences and Their Applications (BMSA). The BMSA was established in 1984 to lead activities in the mathematical sciences at the National Research Council (NRC). The Board consists of 19 members whose backgrounds represent the wide range of the mathematical sciences--core mathematics, applied mathematics, statistics, operations research, scientific computing, and financial and risk analysis. The mission of the Board is to provide expertise drawn from a wide range of mathematical sciences to conduct independent and rigorous assessment of science, engineering, medical, and policy issues in the service of national interest. |
Juliane Mueller Joins CCSEJuliane Mueller, this year's Luis W. Alvarez Postdoctoral Fellow, has joined CCSE where she will continue her work developing optimization algorithms for computationally expensive black-box problems. "This work is important for a wide range of application problems," says Mueller. "There are environmental applications, such as the cleaning up of contaminated groundwater at minimal cost; alternative energy applications, like generating the maximal amount of energy from hydropower dams or kites; or calibration of climate models, which involves finding better model parameters to make predictions agree better with actual observational data." ... [read more] |
|
|
|
BoxLib Proposal Accepted by NERSC Exascale Science Applications Program (NESAP)The recent proposal, Optimization of the BoxLib AMR Framework for Scientific Application Codes, was recently selected by NERSC as one of the 20 projects supported by the NERSC Exascale Science Applications Program (NESAP) As part of the program, the BoxLib team will receive guidance from NERSC, Cray and Intel staff to help prepare BoxLib applications for NERSC's next supercomputer, Cori, which will include the manycore Intel Knights Landing architecture. |
Paper by Emmett, Zhang and Bell Featured on Cover of Combustion Theory and ModelingA recent paper by Matt Emmett, Weiqun Zhang, and John Bell, titled High-Order Algorithms for Compressible Reacting Flow with Complex Chemistry, is featured on the cover of a recent issue of Combustion Theory and Modeling, a journal of the Combustion Institute. This paper describes a numerical algorithm for integrating the multicomponent, reacting, compressible Navier-Stokes equations, targeted for direct numerical simulation of combustion phenomena. |
|
|
|
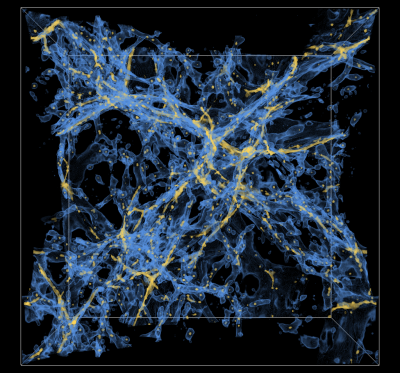
MAESTRO Simulation Included in yt 3.0 DocumentationThe yt community has just announced the release of version 3.0. Yt is an open source, community-developed toolkit for analysis and visualization of volumetric data of all types, with a particular emphasis on astrophysical simulations and nuclear engineering simulations. The recent release contains examples of visualization scripts, including a script for volume rendering of a MAESTRO simulation of astrophysical convection. yt is able to read and interpret CASTRO, MAESTRO, and Nyx plotfiles. |
July 2014 News
CCSE Collaborator Mike Zingale and Students Visit CCSEMike Zingale, a professor at Stony Brook University and long-time CCSE collaborator, brought two of his students west for a productive week-long visits. One of the students, Adam Jacobs, is doing his Ph.D. research using MAESTRO, the BoxLib-based low Mach number solver for astrophysical simulations, and has added OpenACC code to MAESTRO in order to speed up the reaction network for astrophysical flames. Max Katz, also a Ph.D. student of Zingale, is using the BoxLib-based compressible solver, CASTRO, for his thesis research, and has re-written the stellar equation of state (EOS) in OpenACC in order to use the GPU's on the OLCF machine, Titan, to run CASTRO simulations of white dwarf mergers. |
|
|
|
CCSE Collaborator Alejandro Garcia Featured in LA TimesAlejandro Garcia was featured in a story in the Entertainment section of the July 23, 2014 issue of the LA Times in a story titled "Great Read: Physicists, Others Using Science to Help Art of Film Animation." The story describes Garcia's lecture ("Bubble Science") to a team at DreamWorks, in which he described and demonstrated the physics of soap bubbles to artists working on the upcoming movie, "Home". |
Cosmology SciDAC-3 Project Awarded 176 Million Processor Hours Under DOE's ALCC ProgramThe Cosmic Frontier Computational End-Station, led by Salman Habib from Argonne National Laboratory, received 176 million processor hours under DOE's ASCR Leadership Computing Challenge (ALCC) Program, of which 76 million are at NERSC. The ALCC awards time to researchers to pursue high-risk, high-payoff simulation research in energy-mission areas and national emergency mitigation. This allocation will be used for a variety of cosmological simulations, including those using Nyx, a BoxLib-based AMR code created in CCSE. Nyx is being used by researchers to study the Lyman alpha forest; a recent paper discussing recent results can be found here. |
|
|
|
CCSE Collaborator Didem Unat Leaves LBNL to Join Faculty of Koc UniversityDidem Unat, pictured here with John Bell, came to the lab from UCSD as an Alvarez Fellow in 2012, and has just left LBNL to join the faculty of the Computer Science and Engineering Department at Koc University in Istanbul, Turkey. During her time at LBNL she was a member of ExaCT Co-Design center. |
Emmett Gives Talk at SIAM Annual MeetingMatt Emmett presented a talk on Wednesday, July 9, at the SIAM Annual Meeting in Chicago, IL. The talk was titled High-Order Algorithms for Compressible Reacting Flow with Complex Chemistry and describes work with Weiqun Zhang and John Bell on a new numerical algorithm for integrating the multicomponent, reacting, compressible Navier-Stokes equations. The algorithm addresses two shortcomings of previous methods. First, it incorporates an eighth-order narrow stencil approximation of diffusive terms that reduces the communication compared to existing methods and removes the need to use a filtering algorithm to remove Nyquist frequency oscillations that are not damped with traditional approaches. The methodology also incorporates a multirate temporal integration strategy that provides an efficient mechanism for treating chemical mechanisms that are stiff relative to fluid dynamical time scales. The overall methodology is eighth order in space with option for fourth order to eighth order in time. |
|
|
|
Bell Takes New Role in Computational Research DivisionJohn Bell has been given a new role and title -- that of the "Chief Scientist" of the Computational Research Division. Congratulations John! |
Almgren Speaks to UC Merced REU Summer StudentsAnn Almgren gave a talk on "Simulating a Supernova" to a group of college students participating in a summer NSF-sponsored REU (Research Experiences for Undergraduates) program at UC Merced. Ten students and four faculty from UC Merced spent the day visiting LBL and NERSC, and heard talks from Esmond Ng, Ann Almgren, Dan Martin, Dani Ushizima and Chao Yang. |
|
June 2014 News
|
|
Farewell to Mike LijewskiMike Lijewski, a CCSE staff member since 1986, when the group was first formed at LBNL, has taken early retirement. We will miss Mike but wish him the very best! |
Almgren Gives Invited Talk at FVCA7 International Symposium in BerlinAnn Almgren presented an invited plenary talk about "Low Mach Number Modeling of Stratified Flows" at FVCA7 -- the International Symposium of Finite Volumes for Complex Applications VII -- held in Berlin June 15-20,2014. In this talk Almgren described the motivation for, and development of, a low Mach number model to simulate low Mach number astrophysical phenomena, such as the convection in a white dwarf that precedes a Type Ia supernova. |
|
March 2014 News
|
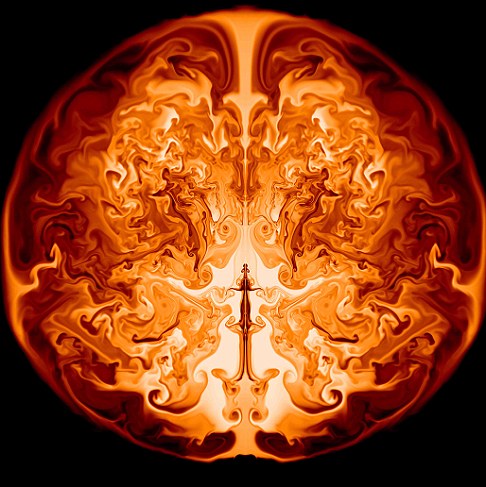
CASTRO Image on Cover of Recent NERSC ReportA visualization of turbulent mixing from a CASTRO simulation of a pulsational-pair supernova (PPSN) is featured on the cover of the recently released "Large Scale Computing and Storage Requirements for High Energy Physics: Target 2017". CASTRO is a BoxLib-based radiation-hydrodynamics AMR code used by researchers to simulate supernovae and other astrophysical phenomena. CASTRO is publicly available on CCSE's Downloads page. |
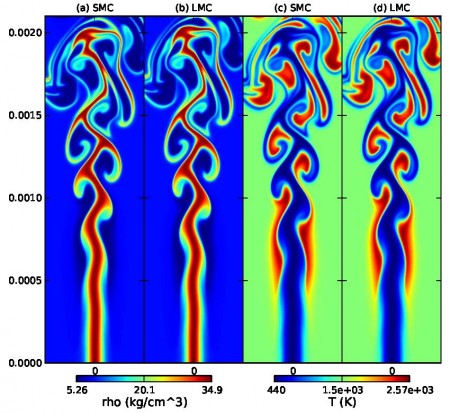
Nyx and LMC Featured in CRAY blog about NERSC's EdisonAccording to the March 20, 2014 CRAY blog about NERSC's new Edison machine, two of the top 10 codes running on Edison today are Nyx and LMC, both BoxLib-based AMR codes created in CCSE. Nyx is a cosmological simulation code used by researchers to study the Lyman alpha forest in a SciDAC-3 project. LMC models the equations of low Mach number combustion to simulate turbulent reacting flows, and is being run as part of the ExACT co-design project. Both typically run on tens of thousands of cores. |
|
|
Nonaka Speaks to Northgate High School Students
As part of Berkeley Lab Computing Sciences' ongoing outreach efforts with bay area high schools,
ten students and three teachers from Northgate high school spent the afternoon of March 14 learning
about NERSC and the roles that math and computation play in scientific efforts at Berkeley Lab.
The event was organized to give the students ideas about career paths in math and science.
|
February 2014 News
|
|
Almgren Gives Invited Talk at NUG 2014: NERSC@40Ann Almgren presented an invited talk about "Low Mach Number Models in Computational Astrophysics" at the 2014 NERSC Users Group Annual Meeting, held February 3-4 at LBNL. In this talk Almgren described the motivation for, and development of, a low Mach number model to simulate low Mach number astrophysical phenomena, such as the convection in a white dwarf that precedes a Type Ia supernova. |
Nyx Simulations Featured As Early Edison Science ResultsLarge-scale Nyx simulations were featured in a recent NERSC story about science results from the "early science" phase of NERSC's just-accepted supercomputer, Edison. Per the article, "Working with 2 million early hours on Edison, [Zarija] Lukic and collaborators performed one of the largest Lyman alpha forest simulations to date: the equivalent of a cube measuring 370 million light years on each side. `With Nyx on Edison we're able - for the first time - to get to volumes of space large enough and with resolution fine enough to create models that aren't thrown off by numerical biases,' he said. Lukic and his collaborators are preparing their results for publication. Lukic expects his work on Edison will become ``the gold standard for Lyman alpha forest simulations'' ... read more |
|
January 2014 News
|
|
Congratulations to Kaushik BalakrishnanKaushik Balakrishnan, a CCSE postdoc for the past several years, has started a postdoctoral position at the Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, CA. We will miss Kaushik but wish him the very best! |
Archive

|
|

|